Although the figures regularly produced by the Nigeria Centre For Disease Control (NCDC) may not reflect the state of the virus in the Nigeria, it does show that COVID-19 is a present reality in the country.

In addition to altering the lives of millions of people around the world, COVID-19 has brought economic activities to a near-standstill. In fact, the World Bank has said “the worst recession since World War II” is imminent. In response to this, countries are now forced to plunge into recovery mode by gradually reopening businesses while curtailing COVID-19 related health risks.
In Nigeria, most organisations have resumed operations but with certain precautionary measures. For instance, staffers in some high profile organisations are subjected to COVID-19 tests before being allowed to resume work. Taking a COVID-19 test for most of these workers can be likened to an examination with an attendant pass or fail outcome.
Workers who test positive for coronavirus are usually sent home or to isolation centers for treatment. However, apart from the immediate health concern associated with being diagnosed with COVID-19, there are other far-reaching socio-economic consequences. These include possible loss of job(s), zero pay and/or future workplace stigmatisation post-recovery. Workers who test negative to the virus, leap for joy and are admitted into the workplace.
But, what does a negative COVID-19 test result really mean? What steps do people need to take after testing negative to the virus? This article responds to these two crucial questions.
What Does a Negative COVID-19 Test Mean?
Knowing that there are different COVID-19 tests is key to understanding the implication of a negative outcome.
There are between two and four different types of COVID- 19 tests. The first is the Molecular or Antigen (Swab) Test. This test involves the use of a long swab (cotton bud) to collect traces of coronavirus from the back of a patient’s throat. A positive result means that the patient has COVID-19, while a negative result indicates that the virus is absent or is present but at very low levels.
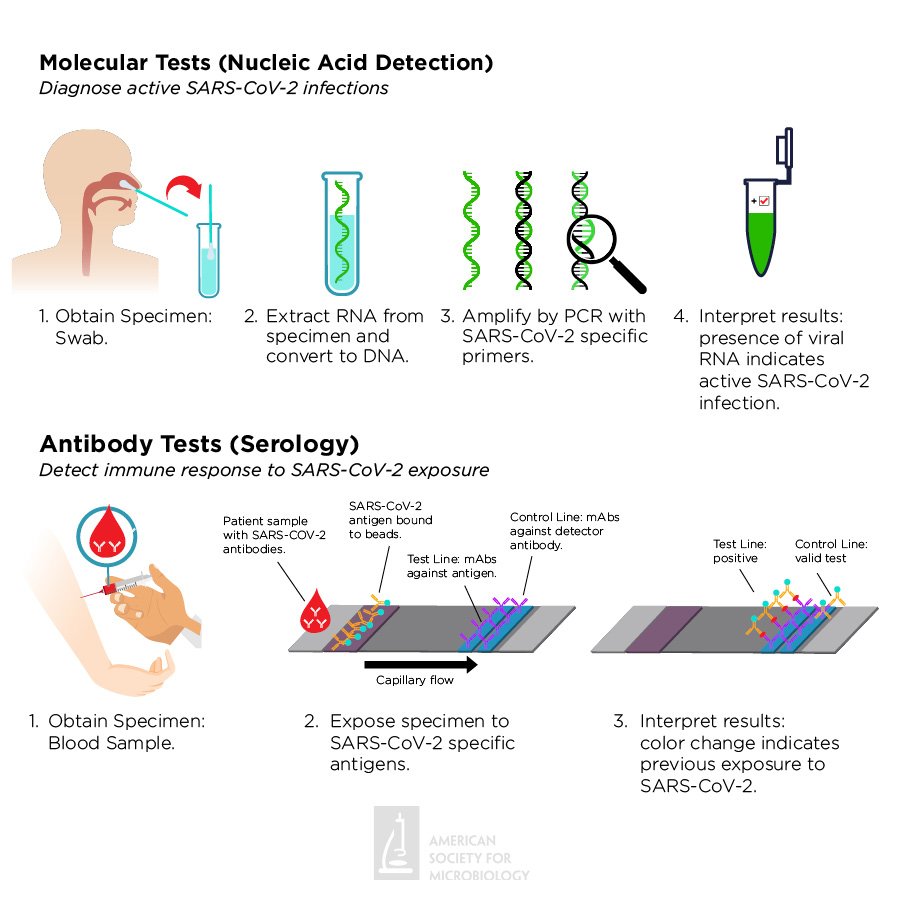
The second type of test is the Antibody or Serology test. Antibodies are types of proteins produced by the immune system to combat infections. Serology tests are usually administered to persons who have been previously exposed to COVID-19 or recovered from ailments associated with the virus. COVID-19 antibody tests are designed to identify immunoglobulins, IgG and IgM in the body.
An antibody test for IgG is usually carried out within 7-10 days after a patient presents with COVID-19. An evidence of IgG antibody in the system means that the patient has previously had the infection and may be immune to reinfection.
The IgM on the other hand, is the first type of antibody produced in the body after a person gets infected. A positive result for IgM means that a patient’s immune system is beginning to combat the virus.
Although having these antibodies may prevent people from being infected with COVID-19, it is not clear how long-term this immunity lasts. This, therefore, means that having a negative COVID-19 test outcome is not grounds for becoming careless or feeling like a superhuman! It instead calls for caution. This brings us to the next question – What steps do people need to take after testing negative to coronavirus?
What You Need To Do Next!
The primary step to take apart from adhering to guidelines on hand washing, wearing of face masks and social distancing, is to enhance one’s immunity response capacity. In other articles we have argued that eating the right foods and exercise are crucial to staying COVID-19 free. Click on these links to read them.
A healthy level of Vitamin D in the body is also crucial to fighting COVID-19. Although there have been many claims regarding the consumption of vitamin supplements to “boost” immunity, there is largely a lack of evidence to support this claim especially if one is healthy. This is with the exception of Vitamin D.
While people in developed climes can obtain the required dose of vitamins from their regular diets, this cannot be said for those in struggling economies like Nigeria. So, in addition to increasing one’s level of Vitamin D intake, regular healthy food intake is also highly recommended. But, let us provide you a bit more information about Vitamin D and its crucial role in the COVID-19 era.
Vitamin D plays an important function in one’s immune response capacity. But, research has shown that about one billion people around the world are Vitamin D deficient. Moreover, with self-isolation and social distancing measures in place, this number is sure to rise owing to lack of exposure to the sun. Natural sunlight is a source of Vitamin D.
Other foods also contain this vitamin and are therefore, highly recommended. These include Oily fish such as Salmon, Sardines and Mackerel.

Vitamin D can also be obtained by eating red meat, liver, egg yolks and cereals.

Elanhub is troubled by the understanding that many people in Nigeria think COVID-19 is a joke. This is despite the fact that some of us now know persons who have recovered from or died as a result of the ailment. Having a negative COVID-19 test outcome is great. But, do all you can to and encourage your family, friends and neighbours to stay healthy.
Follow Elanhub on all our social media platforms and leave your thoughts on this article in the comment section.















